
The SeisComP3 configuration uses a unified schema to configure modules. Modules which use the SeisComP3 libraries can read this configuration directly and share global configuration options like messaging connections, database configurations, logging and much more. There are still some modules that do not use the libraries and are called standalone modules as seedlink, arclink or slarchive. They need wrappers to generate their native configuration when seiscomp update-config is run.
Though it is easy to create the configuration by directly editing the configuration files, it is even more convenient to use a configurator. SeisComP3 ships with a graphical configurator and management tool (scconfig) which makes it easy to maintain module configurations and station bindings even for large networks. It has built-in functionality to check the state of all registered modules and to start and stop them.
The configuration is divided into three parts: stations, bindings and modules.
The trunk configuration files are simple text files where each line is a name-value pair.
Warning
In contrast to previous versions of SeisComP3 the parameter names are now case-sensitive. To check configurations from previous versions regarding case-sensitivity, scchkcfg can be used.
A simple example to assign a parameter "skyColor" the value "blue":
skyColor = blue
Everything following an un-escaped '#' (hash) is a comment and ignored. Blank lines and white spaces are ignored by the parser as well unless quoted or escaped.
skyColor = yellow # This is a comment
# The preceding empty line is ignored and previous setting "yellow"
# is replaced by "blue":
skyColor = blue
Later assignments overwrite earlier ones so the order of lines in the configuration file is important. The file is parsed top-down.
Values can be either scalar values or lists. List items are separated by commas.
# This is a list definition
rainbowColors = red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet
If a value needs to include a comma, white space or any other interpretable character it can either be escaped with backslash (\) or quoted using double quotes ("). White space is removed in unquoted and un-escaped values.
# This is a comment
# The following list definitions have 2 items: 1,2 and 3,4
# quoted values
tuples = "1,2", "3,4"
# escaped values
tuples = 1\,2, 3\,4
Values can extend over multiple lines if a backslash is appended to each line
# Multi-line string
text = "Hello world. "\
"This text spawns 3 lines in the configuration file "\
"but only one line in the value."
# Multi-line list definition
rainbowColors = red,\
orange,\
yellow,\
green, blue,\
indigo, violet
Environment or preceding configuration variables can be used with ${var}.
homeDir = ${HOME}
myPath = ${homeDir}/test
Note
Values are not type-checked. Type checking is part of the application logic and will be handled there. The configuration file parser will not raise an error if a string is assigned to a parameter that is expected to be an integer.
Station meta-data is a fundamental requirement for a seismic processing system and for SeisComP3. Older version used key files to configure available networks and stations. Because the support of response meta-data was very limited, tools were build to add this functionality. In this version the concept of key files for station meta-data has been completely removed from the system. SeisComP3 only handles station meta-data in its own XML format called inventory ML. The task of supporting old key files, dataless SEED and other formats has been out-sourced to external applications (see Inventory synchronization is a two-stage process:).
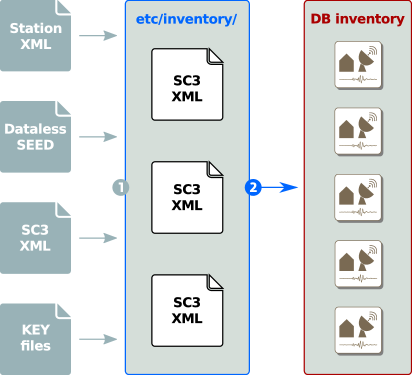
Inventory synchronization is a two-stage process:
External formats are first converted into inventory ML, and then merged and synchronized with the database using seiscomp update-config. All station meta-data are stored in etc/inventory and can be organized as needed. Either one file per network, a file containing the complete inventory or one file for all instruments and one file per station. The update script loads the existing inventory from the database and merges each file in etc/inventory. Finally it removes all unreferenced objects and sends all updates to the database.
The SeisComP3 configuration does not deal with station meta-data anymore. It only configures parameters for modules and module-station associations. The management of the inventory can and should be handled by external tools.
A binding is always connected to a module. The binding configuration directory for each module is etc/key/modulename. It contains either station bindings or profiles.
Bindings are configured and stored in etc/key.
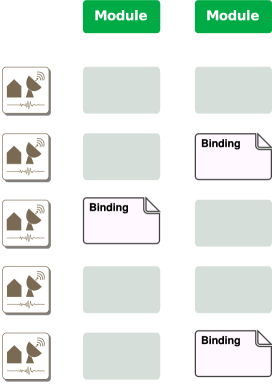
Binding
To bind a station (identified by net_sta) to a module with a set of parameters the first step is to register a module for that station. For that a station key file needs to be created or modified.
Note
To reflect the old framework, a station binding is prefixed with station_ and a profile with profile_.
Let's suppose we have two stations, GE.MORC and GE.UGM and both stations should be configured for SeedLink. Two station key files need to be created (or modified later): etc/key/station_GE_MORC and etc/key/station_GE_UGM.
Both files must contain a line with the module the station is configured for, e.g.:
seedlink
which uses the binding at etc/key/seedlink/station_GE_UGM. When a profile should be used, append it to the module with a colon.
seedlink:geofon
Then the binding at etc/key/seedlink/profile_geofon is read for station GE.UGM. To list all modules a particular station is configured for is very simple by printing the content of the station key file:
$ cat etc/key/station_GE_MORC
seedlink:geofon
global:BH
scautopick
The other way round is a bit more complicated but at least all information is there. To show all stations configured for SeedLink could be done this way:
$ for i in `find etc/key -type f -maxdepth 1 -name "station_*_*"`; do
> egrep -q '^seedlink(:.*){0,1}$' $i && echo $i;
> done
etc/key/station_GE_MORC
etc/key/station_GE_UGM
Where are bindings stored? For standalone modules: nobody knows. It is the task of a standalone module's initialization script to convert the bindings to the module's native configuration.
For all trunk (non-standalone) modules the bindings are written to the SeisComP3 database following the configuration schema. This is done when seiscomp update-config is called. Each module reads the configuration database and fetches all station bindings registered for that module. The database schema used consists of five tables: ConfigModule, ConfigStation, Setup, ParameterSet and Parameter.
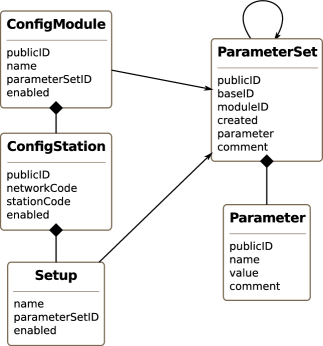
Configuration database schema
Now an example is shown how the tables are actually linked and how the station bindings are finally stored in the database. To illustrate the contents of the objects, the XML representation is used.
<Config>
<module publicID="Config/trunk" name="trunk" enabled="true">
...
</module>
</Config>
A ConfigModule with publicID Config/trunk is created with name trunk. This ConfigModule is managed by the global initialization script (etc/init/trunk.py) and will be synchronized with configured bindings of all trunk modules. The ConfigModule trunk is the one that is actually used by all configurations unless configured otherwise with:
scapp --config-module test
Here scapp would read ConfigModule test. Because a ConfigModule test is not managed by seiscomp update-config it is up to the user to create it.
For each station that has at least one binding, a ConfigStation object is attached to the ConfigModule:
<Config>
<module publicID="Config/trunk" name="trunk" enabled="true">
<station publicID="Config/trunk/GE/UGM"
networkCode="GE" stationCode="UGM" enabled="true">
...
</station>
</module>
</Config>
and finally one Setup per module:
<Config>
<module publicID="Config/trunk" name="trunk" enabled="true">
<station publicID="Config/trunk/GE/UGM"
networkCode="GE" stationCode="UGM" enabled="true">
<setup name="default" enabled="true">
<parameterSetID>
ParameterSet/trunk/Station/GE/UGM/default
</parameterSetID>
</setup>
<setup name="scautopick" enabled="true">
<parameterSetID>
ParameterSet/trunk/Station/GE/UGM/scautopick
</parameterSetID>
</setup>
</station>
</module>
</Config>
Here two setups have been created: default (which is a special case for module global to be backwards compatible) and scautopick where each refers to a ParameterSet by its publicID. The next XML fragment shows the ParameterSet referred by the scautopick setup of station GE.UGM:
<Config>
<parameterSet publicID="ParameterSet/trunk/Station/GE/UGM/scautopick"
created="...">
<baseID>ParameterSet/trunk/Station/GE/UGM/default</baseID>
<moduleID>Config/trunk</moduleID>
<parameter publicID="...">
<name>timeCorr</name>
<value>-0.8</value>
</parameter>
<parameter publicID="...">
<name>detecFilter</name>
<value>
RMHP(10)>>ITAPER(30)>>BW(4,0.7,2)>>STALTA(2,80)
</value>
</parameter>
<parameter publicID="...">
<name>trigOff</name>
<value>1.5</value>
</parameter>
<parameter publicID="...">
<name>trigOn</name>
<value>3</value>
</parameter>
</parameterSet>
</Config>
The mapping to the binding configuration files is 1:1. Each parameter in the configuration file is exactly one parameter in the database and their names are matching exactly.
The concept of global bindings which are specialized for each application is reflected by the baseID of the ParameterSet which points to setup default of station GE.UGM:
<Config>
<parameterSet publicID="ParameterSet/trunk/Station/GE/UGM/default"
created="...">
<moduleID>Config/trunk</moduleID>
<parameter publicID="...">
<name>detecStream</name>
<value>BH</value>
</parameter>
</parameterSet>
</Config>
This ends up with a final configuration for scautopick and station GE.UGM:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| detecStream | BH |
| timeCorr | -0.8 |
| detecFilter | RMHP(10)>>ITAPER(30)>>BW(4,0.7,2)>>STALTA(2,80) |
| trigOff | 1.5 |
| trigOn | 3 |
which is the concatenation of the two files etc/key/global/station_GE_UGM and etc/key/scautopick/station_GE_UGM.
A module is configured by its configuration files either to be used directly or to generate its native configuration. Modules that need to convert the configuration or do not use the default configuration options (see below) are called standalone modules.
Each standalone module tries to read from three configuration files whereas trunk modules try to read six files. Note that configuration parameters defined earlier are overwritten if defined in files read in later:
| File | Standalone | Trunk |
|---|---|---|
| etc/defaults/global.cfg | X | |
| etc/defaults/module.cfg | X | X |
| etc/global.cfg | X | |
| etc/module.cfg | X | X |
| ~/.seiscomp3/global.cfg | X | |
| ~/.seiscomp3/module.cfg | X | X |
The configuration section describes all available configuration parameters for a trunk module. Not all modules make use of all available parameters because they may be disabled, e.g. the messaging component. So the configuration of the messaging server is disabled too.
Extensions add new configuration options to modules. It does not matter how those extensions are used. Commonly a module loads a plugin, which requires additional configuration parameters - these are provided by an extension.
There are currently extensions for the following modules, corresponding to the plugins shown:
| Module | Plugin's |
|---|---|
| scm | email text ncurses |
| kernel | syncarc messaging |
| global | GUI NonLinLoc |
| seedlink | q330 chain |
| arclink | reqhandler |
See the documentation for each module for further information about its extensions.
Type: string
Sets the datacenter ID which is primarily used by Arclink and its tools.
Type: string
Defines the agency ID used to set creationInfo.agencyID in data model objects. Default is GFZ.
Type: string
Organization name used mainly by ArcLink and SeedLink. Default is Unset.
Type: string
Defines the author name used to set creationInfo.author in data model objects.
Type: list:string
Defines a list of modules loaded at startup.
Type: int
Sets the logging level between 1 and 4 where 1=ERROR, 2=WARNING, 3=INFO and 4=DEBUG. Default is 2.
Type: boolean
Enables logging into a log file. Default is true.
Type: boolean
Default is true.
Type: int
Time span after which a log file is rotated. Default is 86400.
Type: int
How many historic log files to keep. Default is 7.
Type: host-with-port
Defines the Spread server name to connect to. Format is host[:port]. Default is localhost.
Type: string
Defines the username to be used. The length is limited to 10 characters with Spread. By default the module name (name of the executable) is used but sometimes it exceeds the 10 character limit and access is denied. To prevent errors set a different username. An empty username will let Spread generate one.
Type: int
The connection timeout in seconds. 3 seconds are normally more than enough. If a client needs to connect to a remote system with a slow connection a larger timeout might be needed. Default is 3.
Type: string
Defines the primary group of a module. This is the name of the group where a module sends its messages to if the target group is not explicitely given in the send call.
Type: string
Defines the message encoding for sending. Allowed values are "binary" or "xml". XML has more overhead in processing but is more robust when schema versions between client and server are different. Default is binary.
Type: list:string
Defines a list of message groups to subscribe to. The default is usually given by the application and does not need to be changed.
Note
database.* Defines the database connection. If no database is configured (which is the default) and a messaging connection is available the application will receive the parameters after the connection is established. Override these values only if you know what you are doing.
Type: string
No description available
Type: string
No description available
Type: string
Default is slink.
Type: string
Default is localhost:18000.
Type: list:string
Default is dbmysql.
Type: boolean
Default is false.
Type: boolean
Default is false.
Type: string
No description available
Type: string
No description available
Type: string
A regular expression of all clients that should handle a command message usually send to the GUI messaging group. Currently this flag is only used by GUI applications to set an artificial origin and to tell other clients to show this origin. To let all connected clients handle the command, ".*$" can be used.
The GUI configuration plugin extends the configuration of graphical user interfaces to various options to adjust the look and feel.
Type: string
Specified the location and the structure of the map tiles to be used. This path is composed of zero or more directives and must include at least one conversion specification which starts with is introduced by the character % followed by a conversion specifier. Valid specifiers are s (replaced by tile ID), l (tile level), c (tile column) and r (tile row). An example for using the OpenStreetMap file structure is /path/to/maps/%l/%c/%r.png. Default is @DATADIR@/maps/world%s.png.
Type: string
Projection of the map tiles. Supported formats are: rectangular and mercator. Default is rectangular.
Note
map.layers.$name.* SeisComP3 supports drawing of arbitrary polygons/polylines. Currently the FEP (@DATADIR@/fep or @CONFIGDIR@/fep) and BNA (@DATADIR@/bna or @CONFIGDIR@/bna) data sets are loaded and may be visualized. While the FEP layer is configured through the layer 'fep', the layer (resp. category) of the BNA data is derived from the directory structure of the BNA folder. In fact the depth of the BNA directory tree is arbitrary and subfolders form subcategories. E.g. the directory tree bna/coastline/europe/germany will generate the categories coastline, coastline.europe, coastline.europe.germany which all may be configured individually. Every undefined property is inherited from the parent category. Unfortunately the configuration GUI only supports editing the top-level category. Subcategories may be configured by editing the configuration file. $name is a placeholder for the name to be used.
Type: boolean
Show/hide the layer Default is true.
Type: boolean
Draws the segment name in the center of the bounding box. For segments read from BNA files the name is extracted from the first part of the header. Default is false.
Type: int
Set or override the rank of the segment. The rank defines the zoom level at which drawing of the segment starts. For segments read from BNA files the name is extracted from the second part of the header if it has the form "rank VALUE", e.g. rank 12. Default is 1.
Type: boolean
If enabled, the bounding box of the segment is drawn. Default is false.
Note
map.layers.$name.pen.* Defines the pen used for drawing the segments of this layer.
Type: double
Pen width Default is 1.0.
Type: color
Pen color Default is 000000ff.
Type: string
Line style. Supported values are: customdashline, dashdotdotline, dashdotline, dashline, dotline, mpenstyle nopen and solidline. Default is solidline.
Note
map.layers.$name.pen.font.* Defines the font of the pen used for drawing the segment name.
Type: int
No description available
Type: string
No description available
Type: boolean
No description available
Type: boolean
No description available
Type: boolean
No description available
Type: boolean
No description available
Note
scheme.* This group defines various color and font options for SeisComp3 graphical user interfaces. There are various conventions to define colors, fonts and gradients. A color is defined in HTML convention. If rgb or rgba is used it must be quoted because the comma is handled as list separator by the configuration. Gradients are configured as lists of tuples where each tuple is colon separated in the form value:color. Color is again a color definition and value is either int or double.
Type: boolean
Show menu bar. Default is true.
Type: boolean
Show status bar. Default is true.
Type: string
Set position if tab bar. An unset value lets the application decide where to place the tab bar. This option might not be supported by all applications. Valid positions are: off, north, south, east, west
Type: color
A general application background color. Can be uses to give each application a different background color. An unset value lets Qt decide.
Type: color
The general color of records/traces. Default is 808080.
Type: color
A general trace color of the alternate trace (eg scheli). Default is 808080.
Type: color
The color of data gaps in trace views. Default is FFFF0032.
Type: color
The color of manual picks. Default is 00FF00.
Type: color
The color of automatic picks. Default is FF0000.
Type: color
The color of picks with undefined state. Default is A0A0A4.
Type: color
The color of disabled picks. Default is A0A0A4.
Type: color
The color of manual arrivals (arrivals that bind manual picks, e.g. residual plot of scolv, manual picker, ...) Default is 00A000.
Type: color
The color of automatic arrivals, Default is A00000.
Type: color
The color of theoretical arrivals. Default is 0000A0.
Type: color
The color of arrivals binding picks with undefined state. Default is A00000.
Type: color
The color of disabled arrivals. Default is A0A0A4.
Type: gradient
The gradient of arrivals residuals. A gradient is defined as a list of tuples separated by colon where the first item is the value and the second is the color. Colors can be given in rgb notation or hex. when rgb is used double quotes are needed to protect the comma inside the rgb definition, e.g. -8:"rgb(0,0,100)", -4:"rgb(0,0,255)", -3:"rgb(100,100,255)", ...
Type: color
The color of active magnitudes. Default is 00A000.
Type: color
The color of inactive magnitudes. Default is 000000.
Type: color
The color of disabled magnitudes. Default is A0A0A4.
Type: gradient
The gradient of magnitude residuals.
Type: color
The color of associated stations (e.g. in scmv). Default is 82AD58.
Type: color
The color of triggered stations.
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
The color of disabled stations.
Type: color
The color of idle stations.
Note
scheme.colors.qc.* The color of QC.delay thresholds in scmv.
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Note
scheme.colors.gm.* The color of ground motion amplitudes in scmv.
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
The color of the selected zoom area (e.g. manual picker). Default is C0C0FFC0.
Type: color
The color of lines in the map (e.g. lines connecting the origin and a station).
Type: color
The color of station outlines in the map.
Type: color
The color grid line color of the map.
Type: color
The color of station annotations.
Type: color
The color of city labels.
Type: color
The color of city outlines.
Type: color
The color of a capital.
Type: color
The color of a "normal" city.
Type: color
The map legend background color.
Type: color
The map legend border color.
Type: color
The map legend text color.
Type: color
The map legend header color.
Type: gradient
The depth gradient. Default is 0:FF0000,50:ffA500,100:FFFF00,250:00FF00,600:0000FF.
Type: boolean
Setting this parameter to true will not interpolate between the depth steps and the color for a depth <= input is used. Default is true.
Note
scheme.colors.originStatus.* The origin status colors (e.g. in event list).
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
No description available
Type: color
The line width of the marker (e.g. picks of manual picker).
Type: font
The general base font of an application. This overrides the default Qt4 application font.
Type: font
No description available
Type: font
No description available
Type: font
No description available
Type: font
No description available
Type: font
No description available
Type: font
No description available
Type: font
No description available
Type: font
No description available
Type: int
The station symbol size (e.g. in scmv).
Type: boolean
Should the vector layer in the map use antialiasing? This improves the visual quality but decreases performance. Default is false.
Type: boolean
Should the map use a bilinear filter? The bilinear filter improves the visual quality but decreases performance slightly. It is only used for static map images. Not while dragging. Default is true.
Type: boolean
Should the map display the grid? Default is true.
Type: boolean
Should the map display the cities? Default is true.
Type: boolean
Should the map display the custom layers? Default is true.
Type: string
SeisComP ships with the rectangular projection build in. Other projections may be provided through plug-ins. Default is Rectangular.
Type: int
The precision of depth values. Default is 0.
Type: int
The precision of distance values. Default is 1.
Type: int
The precision of lat/lon values. Default is 2.
Type: int
The precision of pick times. Default is 1.
Type: boolean
Display distances in km? Default is false.
Type: int
Precision of displayed offset/amp in all trace widgets. Default is 1.
Type: int
Precision of RMS values. Default is 1.
NonLinLoc locator wrapper plugin for SeisComP. NonLinLoc was written by Anthony Lomax (http://alomax.free.fr/nlloc).
Type: string
PublicID creation pattern for an origin created by NonLinLoc. Default is NLL.@time/%Y%m%d%H%M%S.%f@.@id@.
Type: path
Defines the output path for all native NonLinLoc input and output files. Default is /tmp/sc3.nll.
Type: path
The default NonLinLoc control file to use.
Type: double
The default pick error in seconds passed to NonLinLoc if a SC3 pick object does not provide pick time uncertainties. Default is 0.5.
Type: double
Since NLL does not support fixing the depth natively so this feature is emulated by settings the Z grid very tight around the depth to be fixed. This value sets the Z grid spacing. Default is 0.1.
Type: list:string
Defines a list of active profiles to be used by the plugin.
Note
NonLinLoc.profile.$name.* Defines a regional profile that is used if a prelocation falls inside the configured region. $name is a placeholder for the name to be used and needs to be added to NonLinLoc.profiles to become active.
NonLinLoc.profiles = a,b
NonLinLoc.profile.a.value1 = ...
NonLinLoc.profile.b.value1 = ...
# c is not active because it has not been added
# to the list of NonLinLoc.profiles
NonLinLoc.profile.c.value1 = ...
Type: string
earthModelID that is stored in the created origin.
Type: string
methodID that is stored in the created origin.
Type: path
Path to travel time tables (grids).
Type: path
Control file of the current profile. If not set, the default control file will be used instead.
Type: string
Transformation type of the configured region. If not set, GLOBAL is assumed.
Type: list:double
Defines the region values. If transform is GLOBAL 4 values (min_lat, min_lon, max_lat, max_lon) are expected. If transform is SIMPLE then 4 values are expected (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax).
Type: list:double
Only used for transformation SIMPLE. Expects 2 values (lat,lon).
Type: double
Only used for transformation SIMPLE. Defines the rotation around the origin of the defined region.
Type: string
Defines the channel code of the preferred stream used eg by scautopick and scrttv. If no component code is given, 'Z' will be used by default.
Type: string
Defines the location code of the preferred stream used eg by scautopick and scrttv.
Note
amplitudes.* Defines general parameters for amplitudes of a certain type.
Type: boolean
Defines if amplitude calculation is enabled. If disabled then this station will be skipped for amplitudes and magnitudes. Default is true.
Type: boolean
Activates deconvolution for this station. If no responses are configured an error is raised and the data is not processed. Default is false.
Note
amp.$name.* An amplitude profile configures global parameters for a particular amplitude type. The available amplitude types are not fixed and can be extended by plugins. The name of the type must match the one defined in the corresponding AmplitudeProcessor. $name is a placeholder for the name to be used.
Type: boolean
Defines if amplitude calculation of certain type is enabled. Default is true.
Type: double
Defines the mininum SNR to be reached to compute the amplitudes. This value is amplitude type specific and has no global default value.
Type: double
Overrides the default time (relative to the trigger time) of the begin of the noise window used to compute the noise offset and noise amplitude. Each amplitude processor sets its own noise time window and this option should only be changed if you know what you are doing.
Type: double
Overrides the default time (relative to the trigger time) of the end of the noise window used to compute the noise offset and noise amplitude. Each amplitude processor sets its own noise time window and this option should only be changed if you know what you are doing.
Type: double
Overrides the default time (relative to the trigger time) of the begin of the signal window used to compute the final amplitude. Each amplitude processor sets its own signal time window and this option should only be changed if you know what you are doing.
Type: double
Overrides the default time (relative to the trigger time) of the end of the signal window used to compute the final amplitude. Each amplitude processor sets its own signal time window and this option should only be changed if you know what you are doing.
Note
mag.* Defines general parameters for magnitudes of a certain type.
Note
mag.$name.* An magnitude profile configures global parameters for a particular magnitude type. The available magnitude types are not fixed and can be extended by plugins. The name of the type must match the one defined in the corresponding MagnitudeProcessor. $name is a placeholder for the name to be used.
Type: double
Part of the magnitude station correction. The final magnitude value is multiplier*M+offset. This value is usually not required but there for completeness. Default is 1.
Type: double
Part of the magnitude station correction. The final magnitude value is multiplier*M+offset. This value can be used to correct station magnitudes. Default is 0.
Note
picker.BK.* Bkpicker is an implementation of the Baer/Kradolfer picker adapted to SeisComP3. It was created by converting Manfred Baers from Fortran to C++ and inserting it as a replacement for the picker algorithm. The picker interface name to be used in configuration files is "BK".
Type: double
Overrides the default time (relative to the trigger time) of the begin of the signal window used to pick. Default is -20.
Type: double
Overrides the default time (relative to the trigger time) of the begin of the signal window used to pick. Default is 80.
Type: string
BP (Bandpass) is currently the only option. Default is BP.
Type: int
Number of poles. Default is 2.
Type: double
Bandpass lower cutoff freq. in Hz. Default is 5.
Type: double
Bandpass upper cutoff freq. in Hz. Default is 20.
Type: double
Threshold to trigger for pick (c.f. paper), default 10 Default is 10.
Type: double
Threshold for updating sigma (c.f. paper), default 20 Default is 20.
Note
picker.AIC.* AIC picker is an implementation using the simple non-AR algorithm of Maeda (1985), see paper of Zhang et al. (2003) in BSSA. The picker interface name to be used in configuration files is "AIC".
Type: double
Overrides the default time (relative to the trigger time) of the begin of the signal window used to pick. Default is -30.
Type: double
Overrides the default time (relative to the trigger time) of the begin of the signal window used to pick. Default is 10.
Type: string
Overrides the default filter which is "raw". The typical filter grammar can be used.
Type: double
Defines the mininum SNR. Default is 3.
Note
spicker.L2.* L2 is a algorithm to pick S-phases.
Type: double
Overrides the relative start time (relative to the triggering pick) of the begin of the signal window used to pick. Default is 0.
Type: double
Overrides the relative end time (relative to the triggering pick) of the end of the signal window used to pick. Default is 60.
Type: string
Configures the filter used to compute the L2 and to pick the onset after the detector triggered. Default is BW(4,0.3,1.0).
Type: string
onfigures the detector in the filtered L2. Default is STALTA(1,10).
Type: double
The detector threshold that triggers the AIC picker. Default is 3.
Type: double
The time correction (in seconds) added to the final pick time. Default is -0.4.
Type: double
The AIC time window around the detection used to pick. If 0 AIC is not used. Default is 5.
Type: double
Defines the mininum SNR. Default is 15.
Type: string
Define combiner operation for both horizontals (min, max, avg). Default is max.
Type: double
MLh clipping level, in raw counts, eg. 80% of 2^23 = 6710886.
Type: string
Defines attenuation parameters for MLh. Format: "UpToKilometers A B; UpToNextKilometers A B;". Example: "30 nomag; 60 0.018 2.17; 700 0.0038 3.02". The first parameter set "30 nomag" means that up to 30km from the sensor the magnitude should not be calculated.
show help message.
show version information
Use alternative configuration file. When this option is used the loading of all stages is disabled. Only the given configuration file is parsed and used. To use another name for the configuration create a symbolic link of the application or copy it, eg scautopick -> scautopick2.
Load given plugins.
Run as daemon. This means the application will fork itself and doesn't need to be started with &.
Enable/disable self-shutdown because a master module shutdown. This only works when messaging is enabled and the master module sends a shutdown message (enabled with --start-stop-msg for the master module).
Sets the name of the master-module used for auto-shutdown. This is the application name of the module actually started. If symlinks are used then it is the name of the symlinked application.
Sets the name of the master-username of the messaging used for auto-shutdown. If "shutdown-master-module" is given as well this parameter is ignored.
Verbosity level [0..4]. 0:quiet, 1:error, 2:warning, 3:info, 4:debug
Increase verbosity level (may be repeated, eg. -vv)
Quiet mode: no logging output
Limits the logging to a certain component. This option can be given more than once.
Use syslog logging back end. The output usually goes to /var/lib/messages.
Path to lock file.
Send log output to stdout.
Debug mode: --verbosity=4 --console
Use alternative log file.
Overrides configuration parameter connection.username.
Overrides configuration parameter connection.server.
Overrides configuration parameter connection.timeout.
Overrides configuration parameter connection.primaryGroup.
A group to subscribe to. This option can be given more than once.
Overrides configuration parameter connection.encoding.
Sets sending of a start- and a stop message.
List all supported database drivers.
The database connection string, format: service://user:pwd@host/database. "service" is the name of the database driver which can be queried with "--db-driver-list".
The configmodule to use.
Load the inventory database from a given XML file.
Load the configuration database from a given XML file.
List all supported record stream drivers
The recordstream source URL, format: [service://]location[#type]. "service" is the name of the recordstream driver which can be queried with "--record-driver-list". If "service" is not given "file://" is used.
Specify a file as record source.
Specify a type for the records being read.